
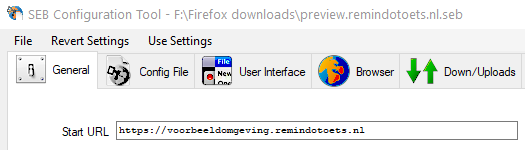
- #Seb configuration tools full
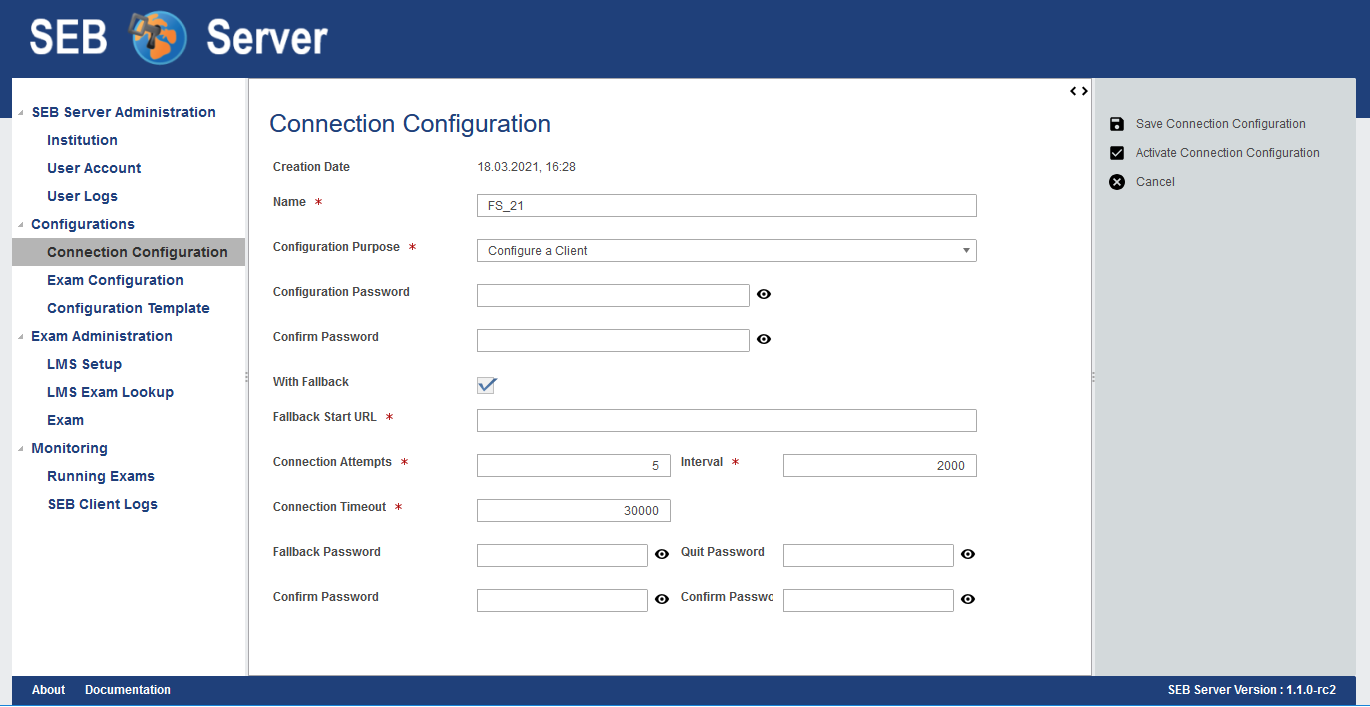
- #Seb configuration tools windows
GPOPermissionsRead – similar to an administrative report, but this one focuses on Authenticated Users missing their permissions. GPOPermissionsAdministrative – this report focuses only on detecting missing Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins permissions and allows you to fix those in no time. It’s basically a one-stop for all permission needs. Finally, it allows you to fix permissions for all those GPOs easily. It also detects GPOs that have Unknown permissions available. It detects GPOs missing read permissions for Authenticated Users, GPOs that miss Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins, or SYSTEM permissions. GPOPermissions – this report provides full permissions overview for all GPOs.
GPOPassword – this report should detect passwords stored in GPOs.GPOLinks – this report summarizes links showing where the GPO is linked, whether it’s linked to any site, cross-domain, or the status of links.
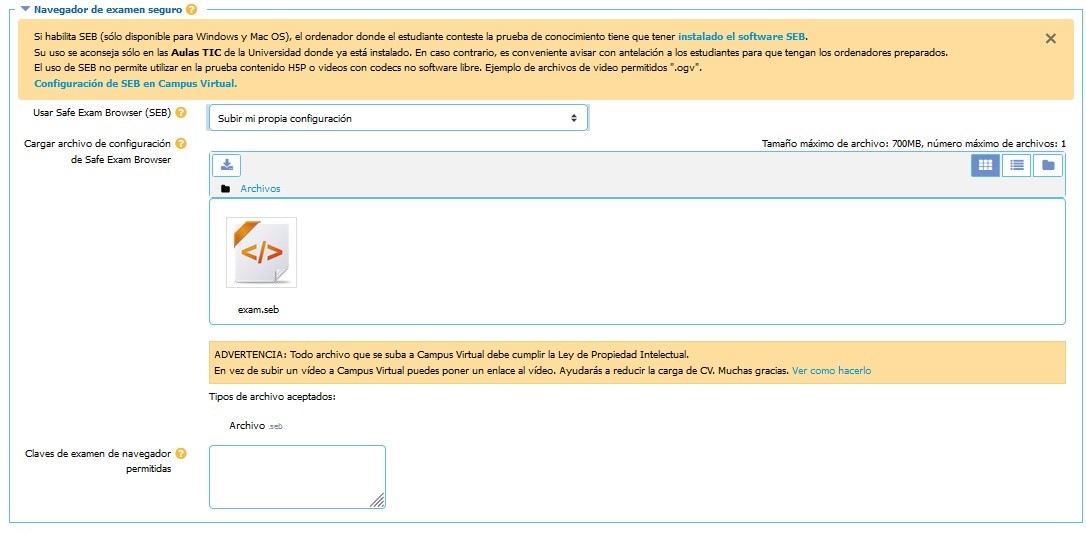
It also can detect GPOs that are not optimized or have potential problems (disabled section, but still settings in it)
GPOList – this report summarizes all group policies focusing on detecting Empty, Unlinked, Disabled, No Apply Permissions GPOs. GPODuplicates – this report detects GPOs that are CNF, otherwise known as duplicate AD Objects, and provides a way to remove them. It then provides you an option to fix it. GPOConsistency – this report detects inconsistent permissions between Active Directory and SYSVOL, verifying that files/folders inside each GPO match permissions as required. This report detects GPOs that are not owned by Domain Admins (in both SYSVOL and AD) and provides a way to fix them. By design, if Domain Admin creates GPO, the owner of GPO is the domain admins group. GPOOwners – this report focuses on GPO Owners. This command can detect that and propose a solution. For example, if a GPO is deleted, sometimes links to that GPO are not properly removed. GPOBrokenLink – this report can detect links that have no matching GPO. Then it provides an easy way to fix it using given step by step instructions. Additionally, it can detect GPO objects that are no longer GroupPolicy objects (how that happens, I’m not able to tell - replication issue, I guess). By broken GPOs, I mean those which exist in AD but have no SYSVOL content or vice versa – have SYSVOL content, but there’s no AD metadata. GPOBroken – this report can detect GPOs that are broken. it’s a tool to eat your Group Policies and tell you what’s wrong with them or give you data for further analysis with zero effort on your side. User logon Kerberos – ADUserLogonKerberos. User changes detailed – ADUserChangesDetailed. Logs Cleared Security – ADLogsClearedSecurity. Logs Cleared Other – ADLogsClearedOther. Group policy changes – ADGroupPolic圜hanges. Group membership changes – ADGroupMembershipChanges. Group changes – Created / Deleted – ADGroupCreateDelete. Group changes – Detailed – ADGroupChangesDetailed. Computer changes – Detailed – ADComputerChangesDetailed. Computer changes – Created / Changed – ADComputerCreatedChanged. Also, check out what happens with your event logs and configure appropriately. Event Log size often gets quickly out of control. Make sure to not select everything unless you require it. Configure as GPO deployed over DC’s OU -> Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Advanced Audit Configuration







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
